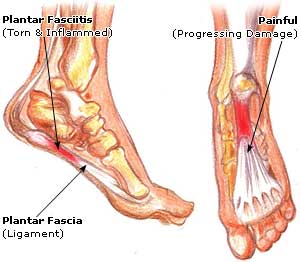
There are actually not one but two unique variations of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital means that you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter compared to the other. As a result of developmental phases of aging, the human brain picks up on the stride pattern and recognizes some variance. The entire body usually adapts by tilting one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch is not grossly abnormal, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and typically won't have a profound effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply fixed, and can eliminate many cases of back problems.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, ordinarily priced at under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Upper back pain is easily the most widespread health problem afflicting men and women today. Around 80 million people are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses huge amounts of money annually due to time lost and output. New and superior treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of reducing the economical influence this issue causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world experience foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts can be of beneficial. The lifts are capable of reducing any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless certified orthopaedic practitioners".
So that you can support the body in a balanced manner, the feet have got a significant job to play. Irrespective of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone in the body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other areas of the body including knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that the right posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply fixed, and can eliminate many cases of back problems.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, ordinarily priced at under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Upper back pain is easily the most widespread health problem afflicting men and women today. Around 80 million people are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses huge amounts of money annually due to time lost and output. New and superior treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of reducing the economical influence this issue causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world experience foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts can be of beneficial. The lifts are capable of reducing any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless certified orthopaedic practitioners".
So that you can support the body in a balanced manner, the feet have got a significant job to play. Irrespective of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone in the body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other areas of the body including knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that the right posture and balance are restored.



 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot, which develops when your big toe starts to angle towards your second toe. The bunion will eventually cause you discomfort and pain. The skin over the lump can become red, blistered or infected. A fluid-filled space called a bursa may also develop under your skin in this area and this can be painful if it becomes inflamed. This is called bursitis. The deformity of your big toe combined with a bunion is sometimes referred to as hallux valgus.
A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot, which develops when your big toe starts to angle towards your second toe. The bunion will eventually cause you discomfort and pain. The skin over the lump can become red, blistered or infected. A fluid-filled space called a bursa may also develop under your skin in this area and this can be painful if it becomes inflamed. This is called bursitis. The deformity of your big toe combined with a bunion is sometimes referred to as hallux valgus.